Tomography, Free Full-Text
Tomography, Free Full-Text
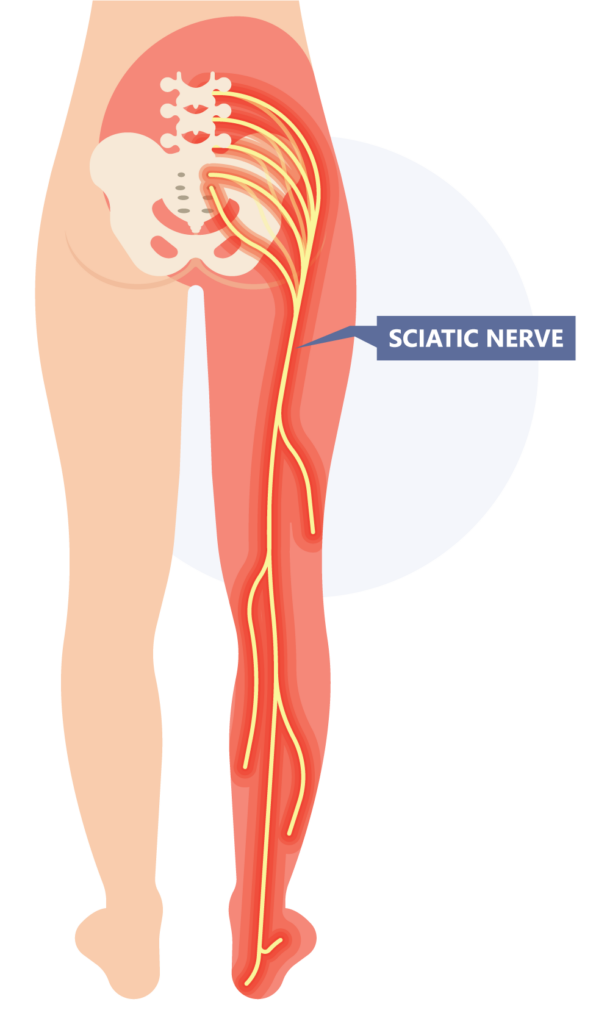
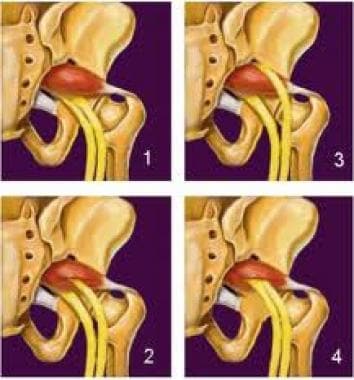
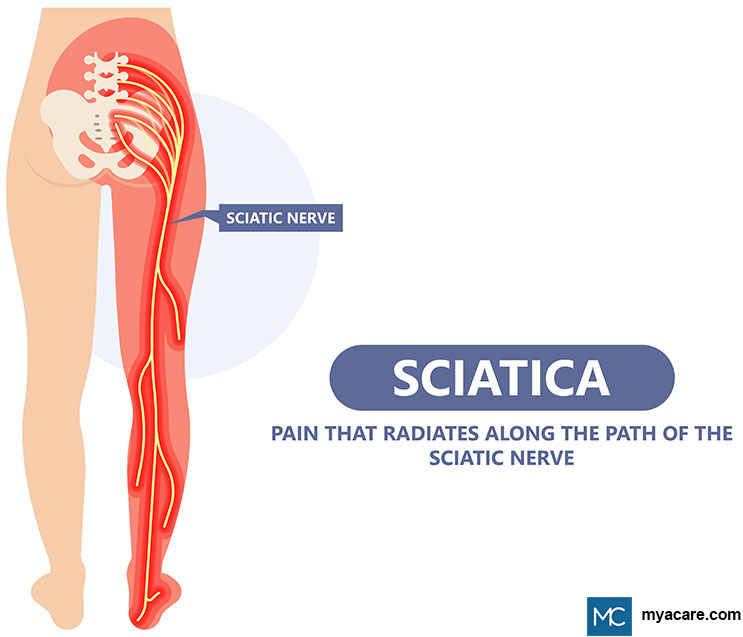
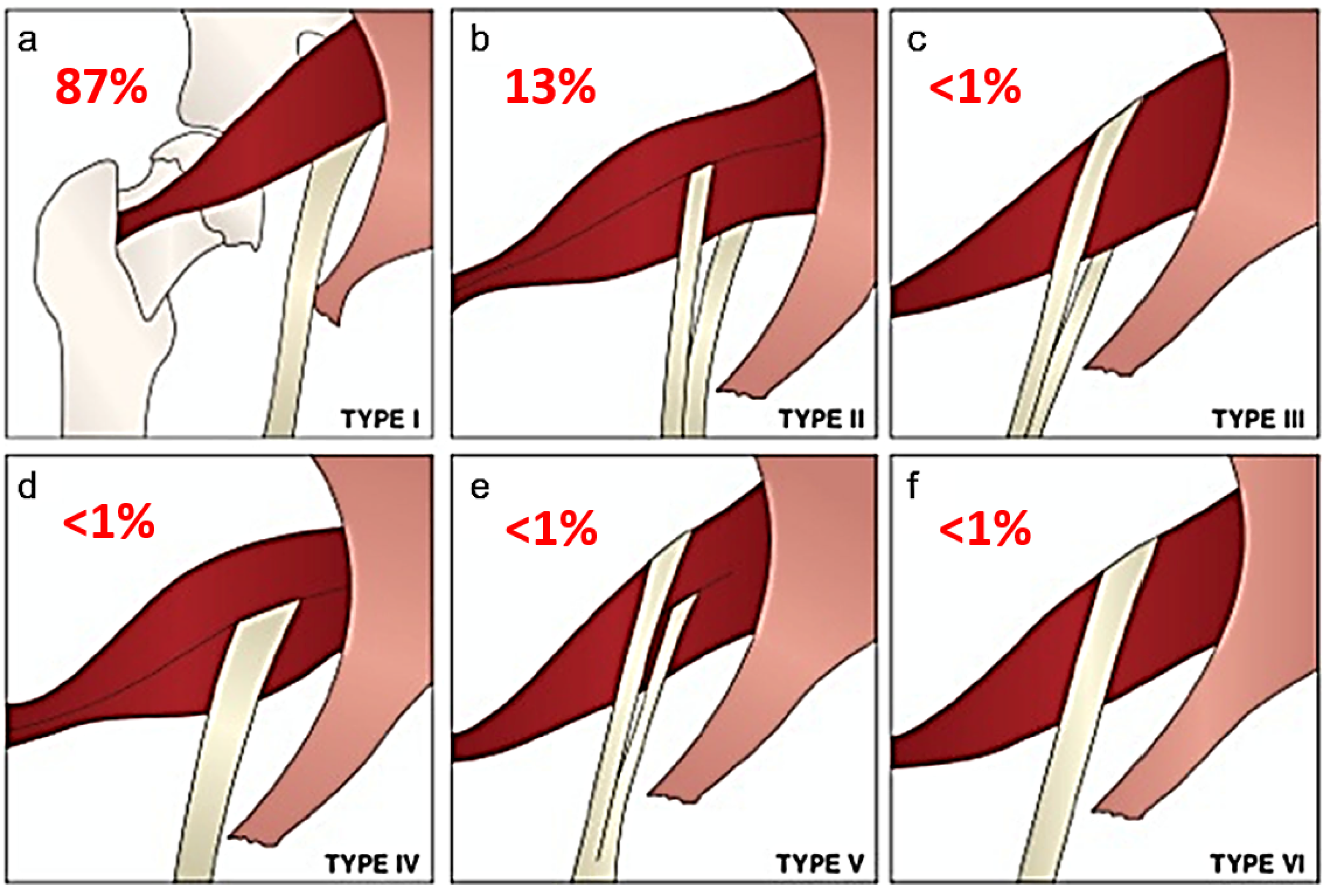
Objective: To assess the prevalence and clinical implications of variant sciatic nerve anatomy in relation to the piriformis muscle on magnetic resonance neurography (MRN), in patients with lumbosacral neuropathic symptoms. Materials and Methods: In this retrospective single-center study, 254 sciatic nerves, from 127 patients with clinical and imaging findings compatible with extra-spinal sciatica on MRN between 2003 and 2013, were evaluated for the presence and type of variant sciatic nerves, split sciatic nerve, abnormal T2-signal hyperintensity, asymmetric piriformis size and increased nerve caliber, and summarized using descriptive statistics. Two-tailed chi-square tests were performed to compare the anatomical variant type and clinical symptoms between imaging and clinical characteristics. Results: Sixty-four variant sciatic nerves were identified with an equal number of right and left variants. Bilateral variants were noted in 15 cases. Abnormal T2-signal hyperintensity was seen significantly more often in variant compared to conventional anatomy (40/64 vs. 82/190; p = 0.01). A sciatic nerve split was seen significantly more often in variant compared to conventional anatomy (56/64 vs. 20/190; p < 0.0001). Increased nerve caliber, abnormal T2-signal hyperintensity, and asymmetric piriformis size were significantly associated with the clinically symptomatic side compared to the asymptomatic side (98:2, 98:2, and 97:3, respectively; p < 0.0001 for all). Clinical symptoms were correlated with variant compared to conventional sciatic nerve anatomy (64% vs. 46%; p = 0.01). Conclusion: Variant sciatic nerve anatomy, in relation to the piriformis muscle, is frequently identified with MRN and is more likely to be associated with nerve signal changes and symptomatology.

PHOTO GALLERY: How COVID-19 Appears on Medical Imaging

Automated CT biomarkers for opportunistic prediction of future cardiovascular events and mortality in an asymptomatic screening population: a retrospective cohort study - The Lancet Digital Health

Total-Body Positron Emission Tomography: Adding New Perspectives to Cardiovascular Research
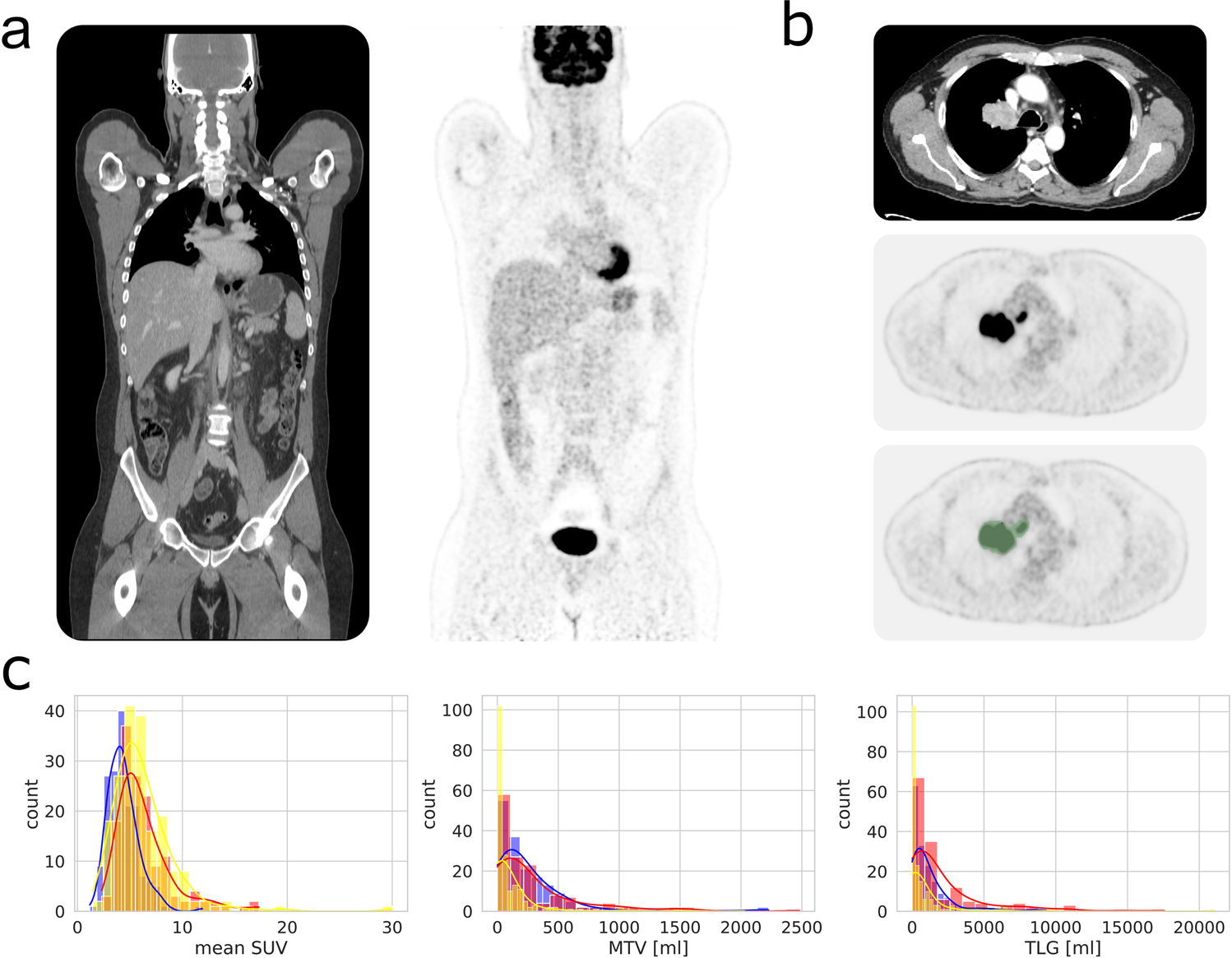
A whole-body FDG-PET/CT Dataset with manually annotated Tumor Lesions

Optical Coherence Tomography and Eye Care
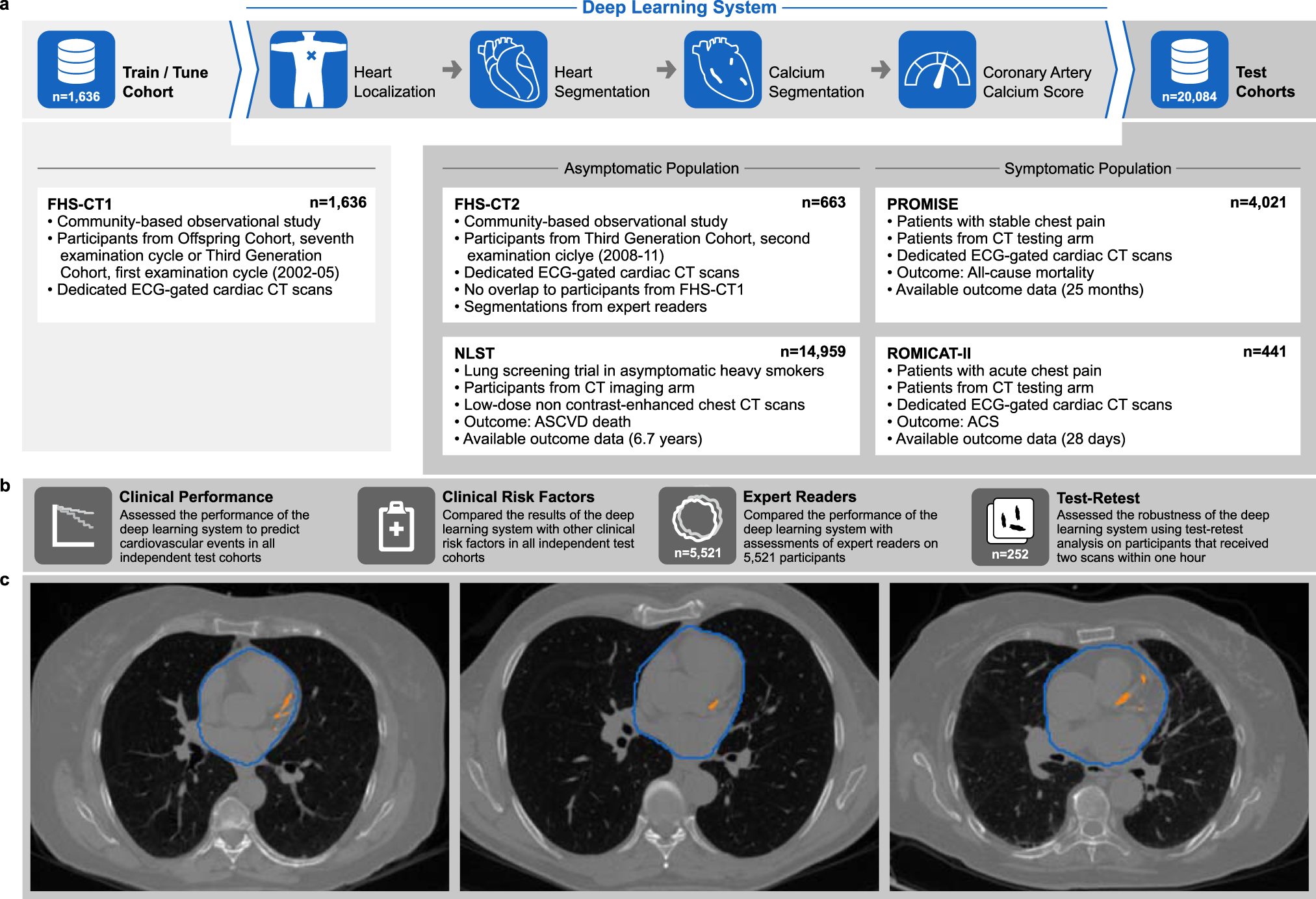
Deep convolutional neural networks to predict cardiovascular risk from computed tomography

CT Imaging Features of 2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV)
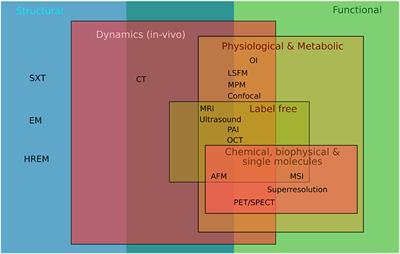
Frontiers Correlated Multimodal Imaging in Life Sciences: Expanding the Biomedical Horizon

Dark-field computed tomography reaches the human scale

Medical imaging - Wikipedia

Immediate total-body CT scanning versus conventional imaging and selective CT scanning in patients with severe trauma (REACT-2): a randomised controlled trial - The Lancet

Sensitive label-free imaging of brain samples using FxClear-based tissue clearing technique - ScienceDirect

Management of Free-Floating Thrombus in Verterbral Artery